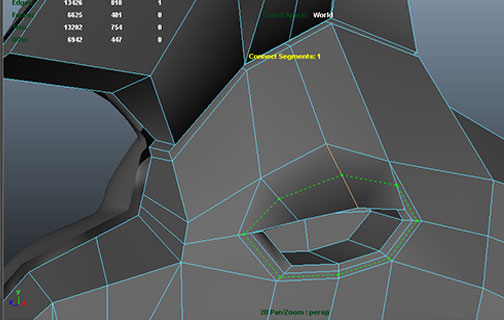
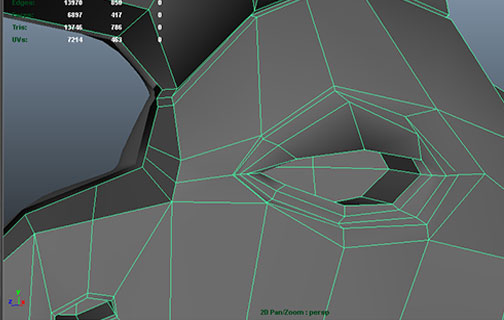
Topology and High Resolution Modeling continued
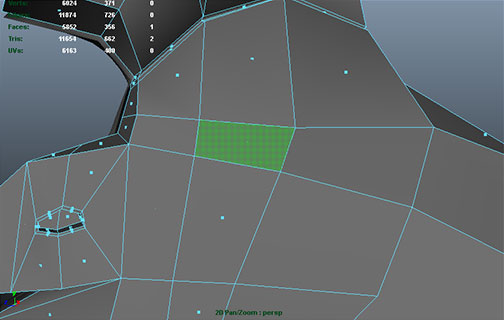
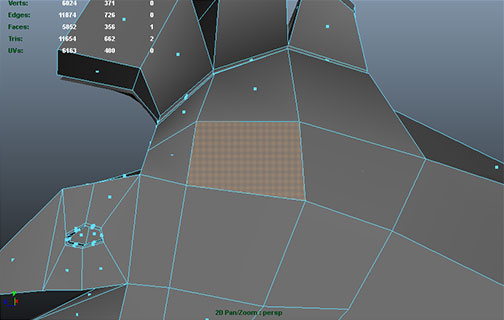
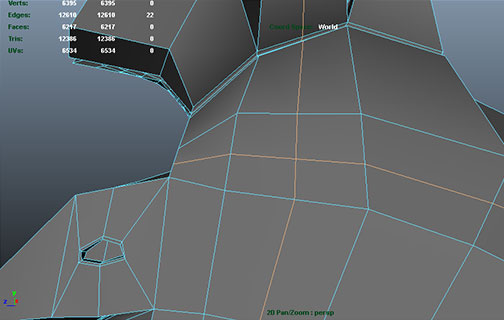
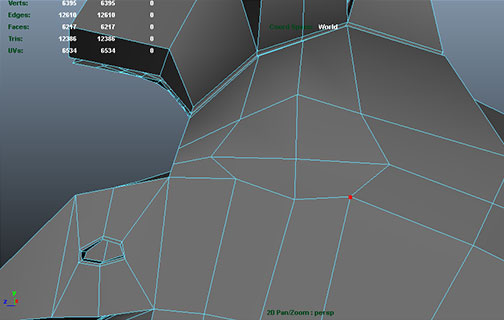
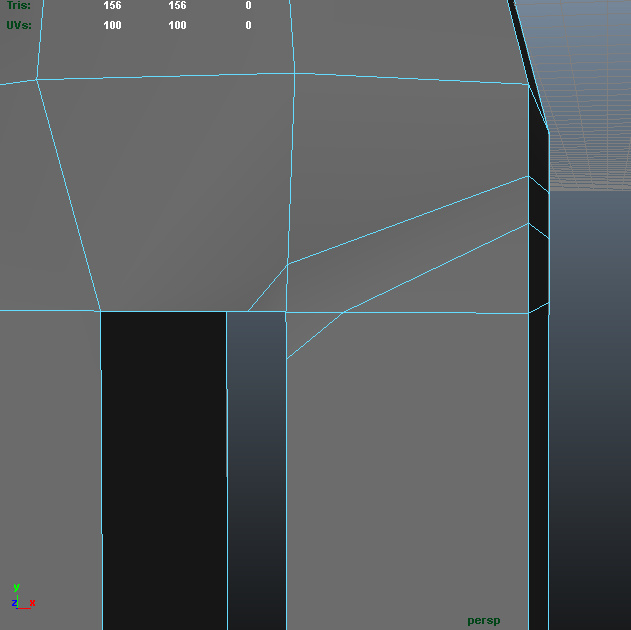
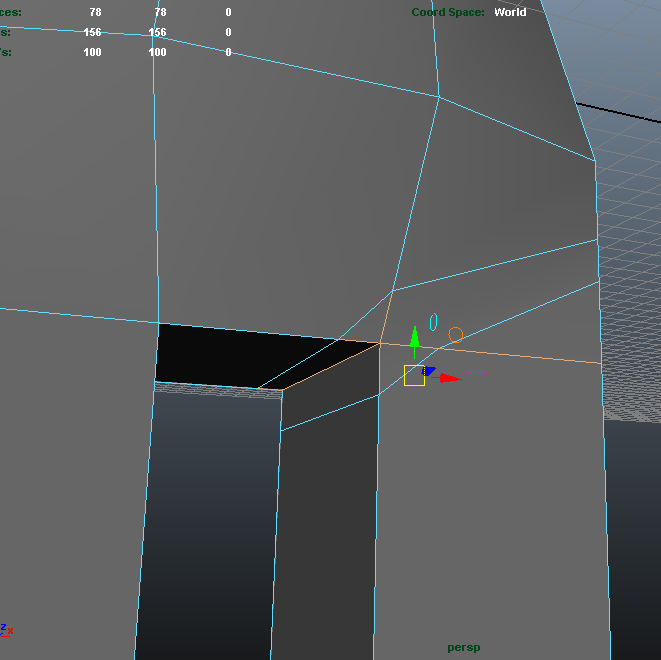
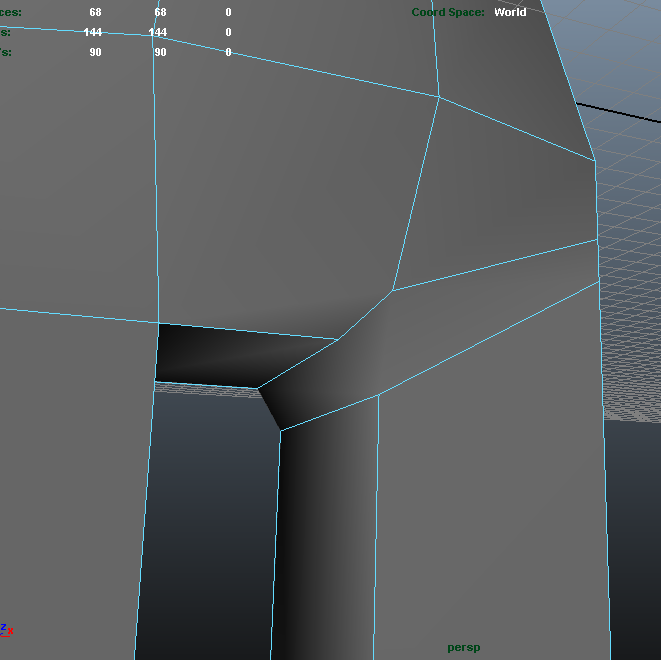
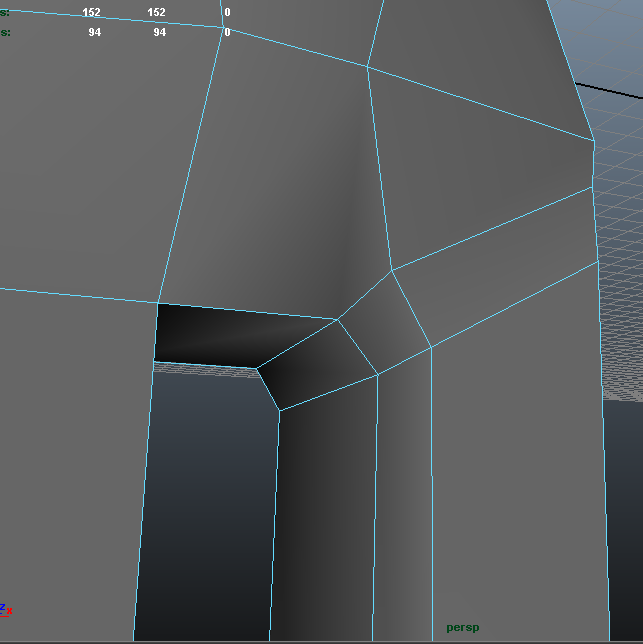
Cubeman exercise
- adding edge loops for shoulder and hip deformation
- laying out foundation for face edge loops
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
1.
|
|
2.
|
|
3.
|
|
4.
|
|
5.
|
|
6.
|
|
7.
|
|
8.
|
|
9.
|
|
10.
|
Sculpting Tools and Soft Select Option
Deformers:
Non-Linear: Bend, Taper, Twist
Lattice, Wrap
Joints and Skeleton:
Joint Tool
Binding Skin
References:
10/05/17
Modeling Environments with Architectural Elements:
General Principles
1. Modular approach: look for repeating patterns, model and texture one sample, replicate.
(Ie windows, balconies, wall panels, base boards, etc). This may mean setting up a group of separate models rather than combining them into one model and merging verts.
2. Model for camera. Ie a model of a room interior may not need one or two walls if they are never seen in the shot. For game modeling, the interiors need to not have visible gaps, so often are completely contained.
3. Avoid computery look: paper thin planes (extrude), perfect edges (bevel), visible borders in repeating textures (use tiling textures).
4. Show environmental and narrative impact: slightly bend window ledges, worn out door steps, chipped off stones, settled brick. Consider set dressing elements to be incorporated.
Tips
-
Setting up Scene Units
-
Using Snapping, Aligning and Measure tools
-
Using Pipe Primitive for arches and windows
-
Beveling Edges
-
Setting up Backface Culling and Normal direction for modeling interiors vs exteriors
-
Using Curves for Polygon Output (pillars, base boards, stair columns)
Use the settings below when converting or outputting curve-based models to Polygons.
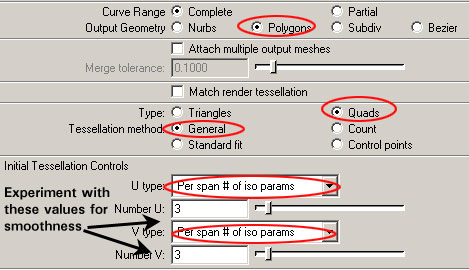
-
Softening and Deteriorating Edges with Modeling and Effects Tools
-
Use Bump, Normal, Specular and Displacement Map to add more surface detail without increasing model resolution
References:
Digital Tutors: Building Urban Environment
Digital Tutors: Interpretive Modeling