fusion 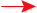
|
 fission fission
|

Lecture XV
Nuclear Energy
fusion 
|
 fission fission
|


Nuclear Power Plants


Chain Reactions To make a sustained chain reaction that operates continuously,
one neutron per fission must be used to
cause another fission.
The neutron must also be slow in order to cause the Uranium-235
nucleus to break up
Fission fragments carry about 80% of the energy released which is
deposited in the moderator and/or coolant.
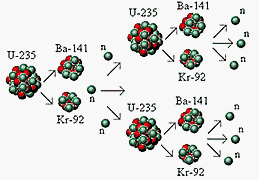
 control rods
are used to absorb neutrons.
control rods
are used to absorb neutrons. water
[and other materials such as carbon compounds] are used to
moderate i.e. slow down, the neutrons enough to allow the
nuclear reactions to occur.
water
[and other materials such as carbon compounds] are used to
moderate i.e. slow down, the neutrons enough to allow the
nuclear reactions to occur.
Controlling the Reaction Recall that on average there are 2.4 neutrons produced
in a Uranium-235 fission reaction.
The proportion of Uranium-235 used in reactors is adjusted to
be 4%. This concentration controls the difficulty of a neutron from a
fission to encounter a Uranium-235 nucleus.
Other Uranium-235 proportions to note are 90% in an atomic bomb and
0.7% in naturally occuring Uranium.
Another measure adopted to reduce the chance that a neutron hits a
Uranium-235 nucleus is the distribution of the fuel rods in
the reactor. They are separated by large gaps of water that
circulates. These large spaces allow some neutrons to escape entirely
from the region around the reactor.
Finally control rods are inserted into the reactor that can
absorb neutrons. By moving the control rods in and out, the rate
of generation of neutron can be controlled.
Conventional Reactor Types Lack of international and business good sense proliferated
designs of nuclear reactors
 too Many Designs for Nuclear Safety!
too Many Designs for Nuclear Safety!
Concentration of Nuclear Power Plants
In 2000 the US Nuclear Regulatory Commission settled on a standard
design AP600 that incorporates the best foreign/US practices and
ideas. But none have been ordered!
A single design


Nuclear Power in the U.S
In the U.S. no new plants have been ordered since 1978.
Reactor construction in the U.S. has stopped. Reactor construction
worldwide has slowed. Why? This is the topic of the next lecture.
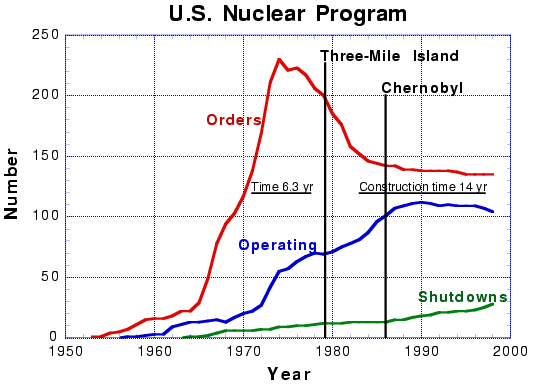
 14 years in the U.S.
14 years in the U.S.
 7 years in Japan
7 years in Japan
 5 years in France
5 years in France
Nuclear Production of Electricity The active nuclear power plants (103) produced 754 billion kWh of
electricity in 2000, 789 billion kWh in 2004 (the record), and
782 billion kWh in 2005. A comparison with other energy sources and
predictions are shown below:
