| Advanced Digital Cinematography | |||||||||||
|
| |||||||||||
 Arts College 755
Arts College 755Call No 02463-2 Req: 752 OSC 1224 Kinnear Fishbowl (rm205) TR 2-348 Winter 2008 05 credits Instructor: Matthew Lewis |
NOTESLinks, examples, odds, and ends from various lectures can be found here as the quarter progresses...Lecture 18Real-time procedural shading
Lecture 16NPR... Another amazing survey by Craig Reynolds Odds+Ends:
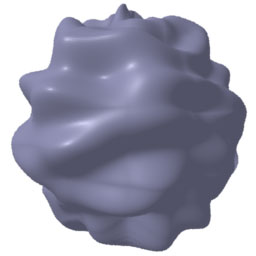


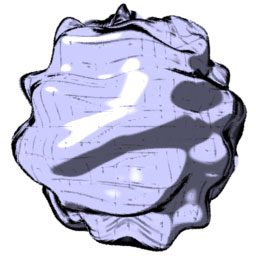 Note cracking prob with cel on displaced sphere. Seems to be related
to filterwidth and filterstep. It's not a displacement bound or
shading rate prob. Suggestions welcomed.
Note cracking prob with cel on displaced sphere. Seems to be related
to filterwidth and filterstep. It's not a displacement bound or
shading rate prob. Suggestions welcomed.









Lecture 15
Lecture 14Occlusion, IBI, HDR, Global Illumination
Lecture 12Solid shaders:

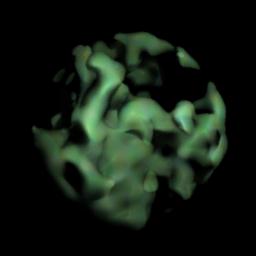
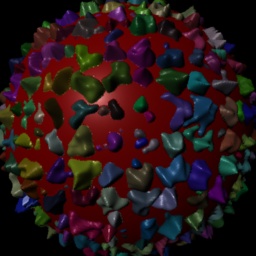 Hypertextures and Isosurfaces
hypertexture.sl
Hypertextures and Isosurfaces
hypertexture.sl

Lecture 081. Displacement in RmanNotes----------------------------------- 2. Simple displacement pattern layer example (rib file)
(rib file)- RmanNotes hetergeneous illumination example -layered displacement illumination example: 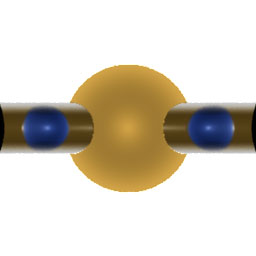 -displacement "Lab assignment":
-displacement "Lab assignment":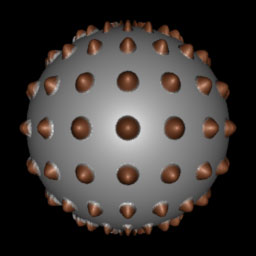

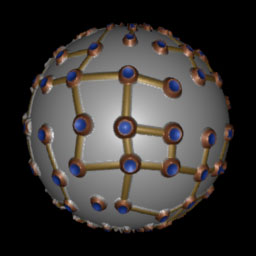
Lecture 06Perlin Noise Talk 1. Color/Shape noise pattern example:
----------------------------------- 2. Incremental noise layer example:








Lecture 04Here's a brief example/hint/snippet for polar coord usage:
topolar2d(s-.5, t-.5, r, th);
r = repeat(r, 8);
th = repeat(th, 4);
layer_opac =
intersection(pulse(0.3, .7, fuzz, r),
pulse(0.25, 0.75, fuzz, th));
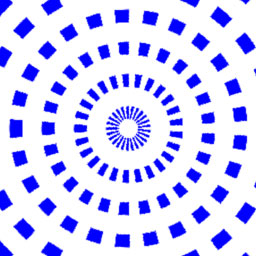 Also a few things about this little example:
Also a few things about this little example:

Lecture 02In class labs:1. BackgroundRead and do Section 2 of assignment one, down through the first five "experiments", to get a quick handle on compiling and viewing shaders.2. Ground/Sky ShaderCreate a shader called "ground_sky". The shader should have one parameter called "location" of type string which specifies the type of image desired. Use the spline() function (see assignment one, experiment 21) to generate simple vertical washes which have a color scheme based on the location parameter. For example, if the location is "desert" the color might go from sienna, to tan, to light blue, to deeper blue from the bottom of the surface to the top. Your shader should handle the following locations: "desert," "arctic," and "sunset." You may add others if you like. Your shader should have some well-defined action if an invalid location is specified by the user and you are not required to perform any illumination calculations in this shader. To get you started, the shader declaration should look like:
surface ground_sky(string location = "desert")
{
/* your code here */
}
Note: RenderMan uses "==" for string comparison, and C-style if {;}
else if {;} else {;} expressions.
Also, set parameter values in your rib file as follows:Surface "myShaderName" "stringParam" "strValue" "numParam" [0.5] "colorP" [0 1 0] 3. Mix CornersWrite a shader called mix_corners which has the following declaration:
surface mix_corners(color upleft = color (1,0,0),
upright = color(0,0,1),
lowleft = color (1,1,0),
lowright = color(0,1,0))
Your shader should interpolate (linearly) between the colors at all
four corners to compute the color at the current point. You can change
the default values to your liking. Big hint: use the mix() function 3
times (see experiment 19.)
4. Color Scheme ShaderExtra-hard challenge bonus problem: Modify the ground_sky shader above to accept three arguments: a base color, a range parameter [0,1], and a string with the value "monochromatic", "analogous", or "complementary". Generate an appropriate color scheme for your ground/sky/horizon based on the parameters specified. |
Assignments Notes Student Work Resources: RManNotes RMRepository RenderMan FAQ Highend3d Deathfall Textbook Pixar 3Delight Aqsis |
|||||||||
|
| |||||||||||